Azure Apps: 7 Powerful Benefits You Can’t Ignore
Thinking about building or moving your apps to the cloud? Azure apps might just be the game-changer you’ve been waiting for. Backed by Microsoft’s robust infrastructure, they offer scalability, security, and seamless integration like no other.
What Are Azure Apps and Why They Matter

Azure apps refer to applications developed, hosted, or managed using Microsoft Azure’s cloud computing platform. These aren’t just ordinary applications—they’re cloud-native, designed to scale on demand, integrate with enterprise systems, and deliver high availability across global regions. Whether you’re building a simple web app or a complex microservices architecture, Azure apps provide the foundation for modern digital transformation.
Defining Azure Apps in the Cloud Ecosystem
Azure apps encompass a wide range of services, including web apps, mobile backends, containerized applications, serverless functions, and APIs. They run on Microsoft’s global network of data centers, ensuring low latency and high reliability. The term ‘Azure apps’ is often used interchangeably with ‘Azure App Services,’ but it extends beyond that to include services like Azure Functions, Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and Azure Logic Apps.
- Azure apps can be developed using virtually any programming language: .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, PHP, and more.
- They support both Windows and Linux environments, giving developers flexibility in deployment.
- Integration with DevOps tools like GitHub Actions and Azure DevOps enables continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD).
“Azure App Service is a fully managed platform that enables developers to build, deploy, and scale web apps quickly.” — Microsoft Azure Official Documentation
How Azure Apps Fit Into Modern Application Development
Modern application development demands agility, scalability, and resilience. Azure apps meet these demands by offering a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) model that abstracts away infrastructure management. This allows developers to focus on writing code rather than managing servers.
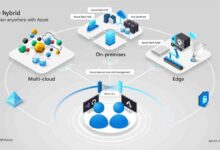
With features like auto-scaling, built-in load balancing, and integrated monitoring, Azure apps reduce operational overhead. They also support hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, making them ideal for enterprises transitioning from on-premises systems.
For example, a retail company can use Azure apps to handle traffic spikes during holiday sales without manually provisioning additional servers. The platform automatically scales up and down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Core Services Behind Azure Apps
Understanding the core services that power Azure apps is essential for leveraging their full potential. Microsoft Azure offers a suite of interconnected services that work together to deliver a seamless app development and deployment experience.
Azure App Service: The Heart of Azure Apps
Azure App Service is the flagship service for hosting web applications, RESTful APIs, and mobile backends. It supports multiple frameworks and provides built-in capabilities for deployment, scaling, and monitoring.
- Supports automated deployments from GitHub, Azure Repos, Bitbucket, and other source control systems.
- Offers staging environments for testing changes before going live.
- Includes built-in SSL certificates, custom domains, and authentication via Azure Active Directory.
One of the standout features of Azure App Service is its ability to run both code and containers. This means you can deploy traditional web apps or modern containerized applications using Docker, all within the same service.
Learn more about Azure App Service: Azure App Service Overview
Azure Functions: Serverless Computing for Azure Apps
Azure Functions enables event-driven, serverless computing. It allows developers to run small pieces of code (functions) in response to triggers like HTTP requests, database changes, or message queues—without managing infrastructure.
- Ideal for background processing, file processing, and integrating with third-party APIs.
- Pays only for the compute time consumed—zero cost when idle.
- Supports languages like C#, JavaScript, Python, Java, and PowerShell.
For instance, an image upload service can trigger an Azure Function to automatically resize the image, apply filters, and store it in Azure Blob Storage—all without a dedicated server running 24/7.
Explore Azure Functions: Azure Functions Documentation
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Scaling Complex Azure Apps
For organizations running containerized applications at scale, Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a powerful option. AKS simplifies the deployment, management, and scaling of Kubernetes clusters, making it easier to run microservices-based Azure apps.
- Automates cluster provisioning, upgrades, and health monitoring.
- Integrates with Azure Monitor, Azure Active Directory, and Azure DevOps.
- Supports hybrid deployments with Azure Arc for managing clusters across on-premises and multi-cloud environments.
AKS is particularly valuable for companies adopting a microservices architecture. Each service can be independently developed, deployed, and scaled, improving agility and fault isolation.
Discover AKS: Azure Kubernetes Service
Benefits of Using Azure Apps for Businesses
Organizations of all sizes are turning to Azure apps to accelerate innovation, reduce costs, and improve reliability. The benefits go beyond technical capabilities—they impact the bottom line and competitive advantage.
Scalability and Performance Optimization
One of the biggest advantages of Azure apps is their ability to scale automatically. Whether you’re experiencing a sudden surge in users or planning for seasonal growth, Azure apps can handle it seamlessly.
- Auto-scaling rules can be based on CPU usage, memory, or custom metrics.
- Global load balancing ensures users are routed to the nearest data center.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) integration improves page load times worldwide.
This scalability is not just about handling traffic—it’s about maintaining performance under pressure. A media company streaming live events can rely on Azure apps to deliver smooth playback to millions of viewers simultaneously.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Security is a top priority for any business, and Azure apps come with enterprise-grade protections built-in. Microsoft invests over $1 billion annually in cybersecurity and employs more than 3,500 security experts.
- Azure apps benefit from advanced threat protection, DDoS mitigation, and encryption at rest and in transit.
- Compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and SOC 2 ensures data privacy and regulatory adherence.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Azure Policy help enforce security best practices across teams.
For financial institutions or healthcare providers handling sensitive data, this level of compliance and security is non-negotiable. Azure apps provide the framework to meet these stringent requirements without additional overhead.
Cost Efficiency and Operational Simplicity
Traditional on-premises applications require significant capital investment in hardware, maintenance, and IT staff. Azure apps shift this to an operational expense model, reducing upfront costs and improving budget predictability.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing means you only pay for what you use.
- Reserved instances and hybrid benefits can reduce costs by up to 40%.
- Automation tools minimize manual intervention, reducing labor costs.
Small startups can launch globally without investing in physical infrastructure, while large enterprises can optimize legacy workloads by migrating them to Azure apps.
How to Get Started with Azure Apps
Starting with Azure apps doesn’t require a massive overhaul. Microsoft provides a clear onboarding path, free tools, and extensive documentation to help developers and businesses get up and running quickly.
Setting Up Your First Azure App
The first step is creating an Azure account. Microsoft offers a free tier with $200 in credits for new users, valid for 30 days, plus access to over 25 always-free services.
- Sign up at Azure Free Account.
- Navigate to the Azure portal and select ‘Create a resource’.
- Choose ‘Web App’ under the App Services category.
- Configure your app name, runtime stack, region, and pricing tier.
- Deploy your code via Git, FTP, or CI/CD pipeline.
Within minutes, your first Azure app will be live and accessible via a public URL. You can then customize settings like custom domains, SSL, and monitoring.
Choosing the Right Deployment Model
Azure apps support multiple deployment models, each suited to different use cases:
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): Ideal for developers who want to focus on code. Azure manages the OS, middleware, and infrastructure.
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS): Offers full control over virtual machines. Suitable for legacy apps that can’t be easily containerized.
- Serverless (Functions): Best for event-driven tasks and microservices. No server management required.
- Containerized (AKS): For complex, scalable microservices architectures.
The choice depends on your team’s expertise, application complexity, and long-term goals. Many organizations start with PaaS and evolve toward hybrid models as their needs grow.
Integrating DevOps with Azure Apps
DevOps practices are crucial for delivering high-quality Azure apps efficiently. Azure provides native tools like Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, and Azure Monitor to streamline the development lifecycle.
- Create automated build and release pipelines.
- Use Azure Monitor to track app performance, logs, and alerts.
- Implement blue-green deployments or canary releases to minimize downtime.
For example, a software team can set up a pipeline where every code commit triggers automated tests and deploys to a staging environment. Once approved, it’s promoted to production with zero manual intervention.
Real-World Use Cases of Azure Apps
The versatility of Azure apps makes them suitable for a wide range of industries and scenarios. From startups to Fortune 500 companies, organizations are leveraging Azure apps to solve real business challenges.
E-Commerce Platforms Scaling with Azure Apps
Online retailers face unpredictable traffic patterns, especially during sales events. Azure apps enable them to scale dynamically and maintain performance.
- A global fashion brand uses Azure App Service to host its e-commerce site, scaling from thousands to millions of users during Black Friday.
- Inventory management is handled via Azure Functions triggered by order events.
- Customer data is securely stored and processed in compliance with GDPR.
The result? Faster page loads, fewer outages, and higher conversion rates.
Healthcare Applications Built on Azure Apps
In healthcare, reliability and data security are paramount. Azure apps provide a compliant, secure environment for patient portals, telemedicine platforms, and medical data analysis.
- A hospital network uses Azure apps to power a telehealth platform, enabling secure video consultations.
- Patient records are encrypted and stored in Azure SQL Database with audit logging.
- AI-powered diagnostics run on Azure Machine Learning, integrated with the main application.
By using Azure apps, healthcare providers improve patient outcomes while meeting strict regulatory requirements.
Enterprise Automation with Azure Logic Apps
Large organizations often have siloed systems that don’t communicate well. Azure Logic Apps enables workflow automation across different platforms without writing code.
- Automate invoice processing by connecting SAP, Outlook, and SharePoint.
- Trigger notifications when a CRM record is updated.
- Sync data between on-premises databases and cloud applications.
One manufacturing company reduced manual data entry by 70% using Azure Logic Apps, freeing up staff for higher-value tasks.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While Azure apps offer numerous benefits, adopting them comes with challenges. Understanding these hurdles and how to address them is key to a successful cloud journey.
Complexity in Migration and Integration
Moving existing applications to Azure apps isn’t always straightforward. Legacy systems may rely on outdated dependencies or proprietary databases that don’t easily translate to the cloud.
- Use Azure Migrate to assess on-premises workloads and plan the migration.
- Leverage Azure Database Migration Service to move SQL Server, Oracle, or MySQL databases.
- Adopt a phased approach: start with non-critical apps to test the waters.
For example, a bank migrated its customer portal in stages, first moving static content, then dynamic pages, and finally integrating with core banking systems—all using Azure apps as the backbone.
Cost Management and Optimization
Without proper oversight, cloud costs can spiral out of control. It’s easy to over-provision resources or leave unused services running.
- Use Azure Cost Management + Billing to track spending by resource, team, or project.
- Set up budgets and alerts to prevent overspending.
- Right-size virtual machines and scale down during off-peak hours.
One company reduced its monthly Azure bill by 35% simply by identifying and shutting down idle development environments.
Security and Identity Management
With more services in the cloud, securing access becomes more complex. Misconfigured permissions can lead to data breaches.
- Implement Azure Active Directory (AAD) for centralized identity management.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users.
- Use Azure Security Center to detect vulnerabilities and recommend fixes.
Regular audits and automated policy enforcement help maintain a strong security posture across all Azure apps.
Future Trends Shaping Azure Apps
The landscape of cloud computing is evolving rapidly, and Azure apps are at the forefront of innovation. Staying ahead of trends ensures your applications remain competitive and future-ready.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Microsoft is deeply integrating AI into Azure apps. From cognitive services to custom machine learning models, developers can now add intelligent features with minimal effort.
- Use Azure Cognitive Services for vision, speech, language, and decision-making APIs.
- Train custom models using Azure Machine Learning and deploy them as web services.
- Integrate AI-powered chatbots into customer support apps using Azure Bot Service.
A retail app can use AI to recommend products based on user behavior, increasing engagement and sales.
Edge Computing and Hybrid Cloud
As IoT devices proliferate, processing data closer to the source becomes critical. Azure apps are extending to the edge with services like Azure IoT Edge and Azure Arc.
- Run Azure apps on edge devices for real-time analytics and decision-making.
- Manage hybrid environments from a single control plane using Azure Arc.
- Ensure low-latency responses for applications like autonomous vehicles or smart factories.
This convergence of cloud and edge computing enables new use cases that were previously impossible.
Sustainability and Green Cloud Computing
Sustainability is becoming a key factor in technology decisions. Microsoft has committed to being carbon negative by 2030, and Azure apps play a role in this vision.
- Optimized data centers reduce energy consumption.
- Azure Sustainability Calculator helps estimate the carbon footprint of your apps.
- Efficient resource utilization lowers both costs and environmental impact.
By choosing Azure apps, businesses contribute to a greener future while improving efficiency.
Best Practices for Managing Azure Apps
To get the most out of Azure apps, it’s important to follow industry best practices. These guidelines help ensure reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Implement Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Managing Azure apps manually is error-prone and unsustainable at scale. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) allows you to define and deploy resources using code.
- Use tools like Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates or Terraform.
- Version control your infrastructure just like application code.
- Enable reproducible environments for development, testing, and production.
This approach reduces configuration drift and accelerates deployment cycles.
Monitor and Optimize Performance
Even the best-designed Azure apps can suffer from performance issues if not monitored properly.
- Enable Azure Monitor to collect logs, metrics, and application insights.
- Set up alerts for high CPU, memory usage, or failed requests.
- Use Application Insights to trace requests across microservices.
Proactive monitoring helps identify bottlenecks before users are affected.
Secure by Design: Embed Security from the Start
Security shouldn’t be an afterthought. Azure apps should be designed with security principles from day one.
- Follow the principle of least privilege when assigning roles.
- Encrypt sensitive data and manage keys with Azure Key Vault.
- Regularly update dependencies and patch vulnerabilities.
By embedding security into the development lifecycle, organizations reduce risk and build trust with users.
What are Azure apps?
Azure apps are applications built, hosted, or managed on Microsoft Azure’s cloud platform. They include web apps, mobile backends, serverless functions, and containerized services, offering scalability, security, and integration with enterprise systems.
How much does it cost to run Azure apps?
Costs vary based on usage, but Azure offers a free tier with $200 in credits for new users. Pricing is pay-as-you-go, with options for reserved instances to reduce long-term costs. You only pay for the resources you consume.
Can I migrate my existing app to Azure apps?
Yes, Azure provides tools like Azure Migrate and Database Migration Service to assess, plan, and execute migrations. Many organizations successfully move legacy applications to Azure apps with minimal downtime.
Are Azure apps secure?
Yes, Azure apps benefit from Microsoft’s enterprise-grade security, including encryption, threat detection, DDoS protection, and compliance with global standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
What programming languages can I use with Azure apps?
You can use virtually any language, including .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, PHP, and Go. Azure apps support both Windows and Linux environments, giving developers maximum flexibility.
From startups to global enterprises, Azure apps are transforming how applications are built and delivered. With powerful services like App Service, Functions, and AKS, businesses can achieve scalability, security, and innovation at speed. By following best practices in deployment, monitoring, and security, organizations can fully harness the potential of Azure apps. As AI, edge computing, and sustainability shape the future, Azure apps remain at the forefront of cloud innovation—making them an essential tool for any modern digital strategy.
Further Reading: